Zero To Hero Guide : : For CEPH CLUSTER PLANNING
What it is all about :
If you think or discuss about Ceph , the most common question strike to your mind is "What Hardware Should I Select For My CEPH Storage Cluster ?" and yes if you really thought of this question in your mind , congratulations you seems to be serious about ceph technology and You should be because CEPH IS THE FUTURE OF STORAGE.
Ceph runs on Commodity hardware , Ohh Yeah !! everyone now knows it . It is designed to build a multi-petabyte storage cluster while providing enterprise ready features. No single point of failure , scaling to exabytes , self managing and self healing ( saves operational cost ) , runs on commodity hardware ( no vendor locking , saves capital investment )
Ceph Overview :-
The sole of ceph storage cluster is RADOS ( Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Store ). Ceph uses powerful CRUSH ( Controlled Replication Under Scalable Hashing ) algorithm for optimize data placement , self managing and self healing. The RESTful interface is provided by Ceph Object Gateway (RGW) aks Rados GateWay and virtual disks are provisioned by Ceph Block Device (RBD)
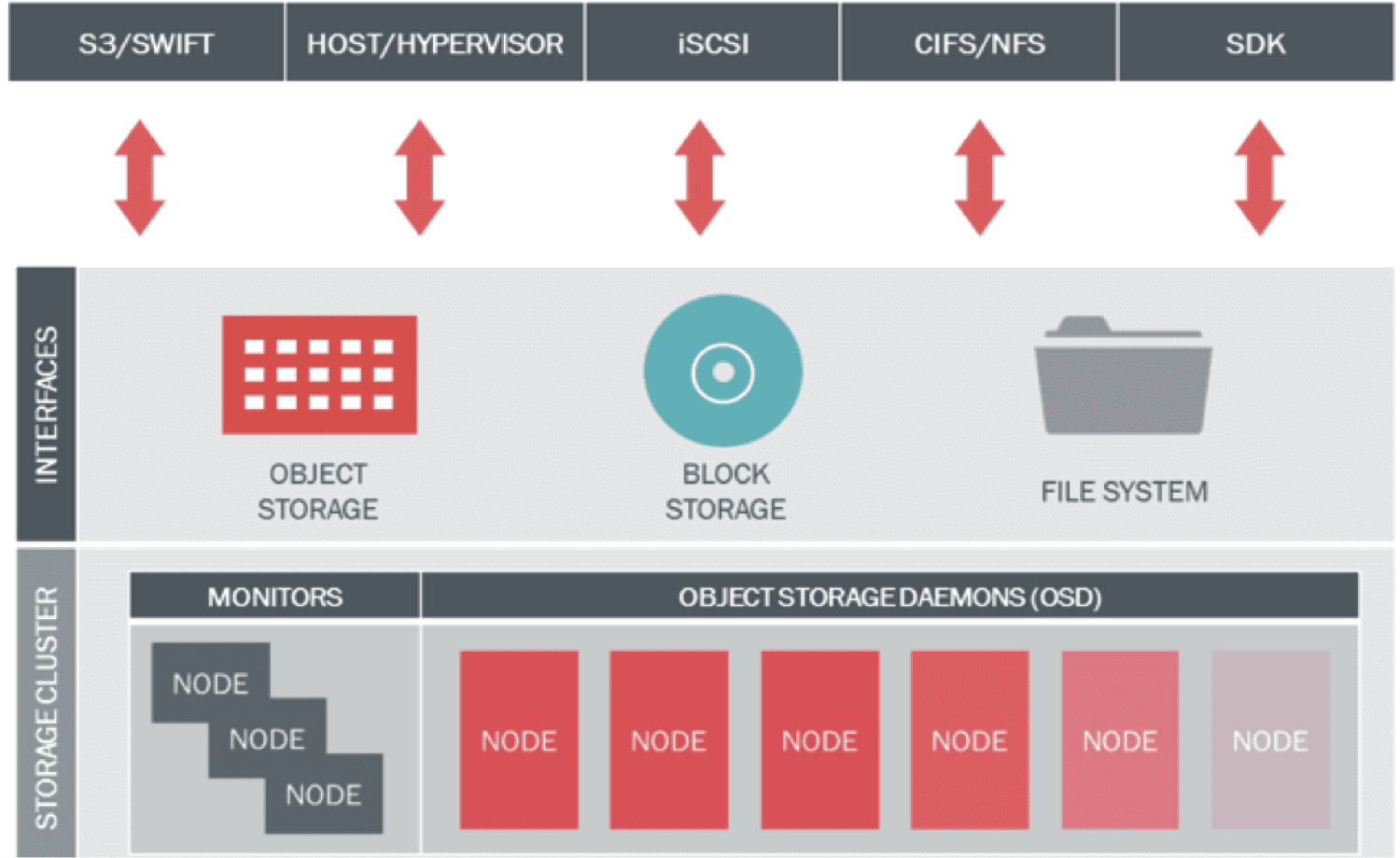 |
| Ceph Overview - Image Credit : Inktank |
Ceph Components :-
# Ceph OSD ( Object Storage Daemons ) storage data in objects , manages data replication , recovery , rebalancing and provides stage information to Ceph Monitor. Its recommended to user 1 OSD per physical disk.
# Ceph MON ( Monitors ) maintains overall health of cluster by keeping cluster map state including Monitor map , OSD map , Placement Group ( PG ) map , and CRUSH map. Monitors receives state information from other components to maintain maps and circulate these maps to other Monitor and OSD nodes.
# Ceph RGW ( Object Gateway / Rados Gateway ) RESTful API interface compatible with Amazon S3 , OpenStack Swift .
# Ceph RBD ( Raw Block Device ) Provides Block Storage to VM / bare metal as well as regular clients , supports OpenStack and CloudStack . Includes Enterprise features like snapshot , thin provisioning , compression.
# CephFS ( File System ) distributed POSIX NAS storage.
Few Thumb Rules :-
- Run OSD on a dedicated storage node ( server with multiple disks ) , actual data is stored in the form of objects.
- Run Monitor on a separate dedicated hardware or coexists with ceph client nodes ( other than OSD node ) such as RGW , CephFS node . For production its recommended to run Monitors on dedicated low cost servers since Monitors are not resource hungry.
Monitor Hardware Configuration :-
Monitor maintains health of entire cluster , it contains PG logs and OSD logs . A minimum of three monitors nodes are recommended for a cluster quorum. Ceph monitor nodes are not resource hungry they can work well with fairly low cpu and memory. A 1U server with low cost processor E5-2603,16GB RAM and 1GbE network should be sufficient in most of the cases. If PG,Monitor and OSD logs are storage on local disk of monitor node , make sure you have sufficient amount of local storage so that it should not fill up.
Unhealthy clusters require more storage for logs , can reach upto GB and even hundreds of GB if the cluster is left unhealthy for a very long time . If verbose output is set on monitor nodes, then these are bound to generate huge amount of logging information. Refer ceph documentation for monitor log setting.
Its recommended to run monitor on distant nodes rather on all on all one node or on virtual machines on physical separated machines to prevent single point of failure.
The Planning Stage :-
Deploying a ceph cluster in production requires a little bit Homework , you should gather the below information so that you can design a better and more reliable and scalable ceph cluster to fit in your IT needs. These very specific to your needs and your IT environment. This information will help you to design your storage requirement better.
Business Requirement
Budget ?
Do you need Ceph cluster for day to day operation or SPECIAL
Technical Requirement
What applications will be running on your ceph cluster ?
What type of data will be stored on your ceph cluster ?
Should the ceph cluster be optimized for capacity and performance ?
What should be usable storage capacity ?
What is expected growth rate ?
How many IOPS should the cluster support ?
How much throughput should the cluster support
How much data replication ( reliability level ) you need ?
Collect as much information as possible during the planning stage , the will give all the answers required to construct a better ceph cluster.
The Physical Node and clustering technique:-
In addition to above collected information , also take into account the rack density and power budget , data center space pace cost to size the optimal node configuration. Ceph replicated data across multiple nodes in a storage cluster to provide data redundancy and higher availability. Its important to consider.
- Should the replicated node be on the same rack or multiple racks to avoid SPOF ?
- Should the OSD traffic stay within the rack or span across rack in a dedicated or shared network ?
- How many nodes failure can be tolerated ?
- If the nodes are separated out across multiple racks network traffic increases and the impact of latency and the number of network switch hops should be considered.
Ceph will automatically recover by re-replicating data from the failed nodes using secondary copies present on other nodes in cluster . A node failure thus have several effects.
- Total cluster capacity is reduced by some fractions.
- Total cluster throughput is reduced by some fractions.
- The cluster enters a write heavy recovery processes.
A general thumb of rule to calculate recovery time in a ceph cluster given 1 disk per OSD node is :
Recovery Time in seconds = disk capacity in Gigabits / ( network speed *(nodes-1) )
# POC Environment -- Can have a minimum of 3 physical nodes with 10 OSD's each. This provides 66% cluster availability upon a physical node failure and 97% uptime upon an OSD failure. RGW and Monitor nodes can be put on OSD nodes but this may impact performance and not recommended for production.
# Production Environment -- a minimum of 5 physically separated nodes and minimum of 100 OSD @ 4TB per OSD the cluster capacity is over 130TB and provides 80% uptime on physical node failure and 99% uptime on OSD failure. RGW and Monitors should be on separate nodes.
Based on the outcome of planning phase and physical nodes and clustering stage you have a look on the hardware available in market as per your budget.
OSD CPU selection :-
< Under Construction ... Stay Tuned >